Installation on GCP
In this guide, you will set up Nephio with:
- Management Cluster: GKE Standard with auto scaling enabled
- Cluster Provisioner: Kubernetes Config Connector (KCC), hosted as a managed service via Config Controller (CC).
- Workload Clusters: GKE
- GitOps Tool: Config Sync
- Git Provider: Google Cloud Source Repositories will be the git provider for cluster deployment repositories. Some external repositories will be on GitHub.
- Web UI Auth: Google OAuth 2.0
- Ingress/Load Balancer: Ingress with a GKE-specific FrontEndConfig to provide HTTP-to-HTTPS redirection will be used to access the Nephio Web UI.
Additionally, this guide makes the following simplifying choices:
- All resources (Nephio management cluster, Config Controller, and workload clusters) will be in the same GCP project.
- All clusters attached to the default VPC as their primary VPC.
- All clusters will be created in the same region or zone.
It is certainly possible to set up Nephio without these assumptions - that is left as an exercise for the reader.
Prerequisites
In addition to the general prerequisites, you will need:
- A GCP account. This account should have enough privileges to create projects, enable APIs in those projects, and create the necessary resources.
- Google Cloud CLI (gcloud) installed and set up on your workstation.
- git installed on your workstation.
Setup Your Environment
To make the instructions (and possibly your life) simpler, you can create a gcloud configuration and a project for Nephio.
In the commands below, several environment variables are used. You can set them to appropriate values for you. Set LOCATION to a region to create a regional Nephio management cluster, or to a zone to create a zonal cluster. Regional clusters have increased availability but higher resource demands.
- PROJECT is an existing project ID, or the ID to use for a new project.
- ACCOUNT should be your Google account mentioned in the prerequisites.
- REGION is the region for your Config Controller. See [this link] for the list of supported regions.
- LOCATION is the location (region or zone) for your Nephio management cluster as well as any workload clusters you create. Setting this will not limit you to this location, but it will be what is used in this guide. Note that Config Controller is always regional.
- WEBUIFQDN is the fully qualified domain name you would like to use for the web UI.
- MANAGED_ZONE is the GCP name for the zone where you will put the DNS entry for WEBUIFQDN. Note that it is not the domain name, but rather the managed zone name used in GCP - for example, my-zone-name, not myzone.example.com.
Set the environment variables:
PROJECT=your-nephio-project-id
ACCOUNT=your-gcp-account@example.com
REGION=us-central1
LOCATION=$REGION
WEBUIFQDN=nephio.example.com
MANAGED_ZONE=your-managed-zone-name
First, create the configuration. You can view and switch between gcloud configurations with
gcloud config configurations list and gcloud config configurations activate.
gcloud config configurations create nephio
The output is similar to:
Created [nephio].
Activated [nephio].
Next, set the configuration to use your account.
gcloud config set account $ACCOUNT
The output is similar to:
Updated property [core/account].
Now, create a project for your Nephio resources. The instructions here work in the simplest environments. However, your organization may have specific processes and method for creating projects. See the GCP project creation documentation or consult with the GCP administrators in your organization.
gcloud projects create $PROJECT
The output is similar to:
Create in progress for [https://cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com/v1/projects/your-nephio-project-id].
Waiting for [operations/cp.6666041359205885403] to finish...done.
Enabling service [cloudapis.googleapis.com] on project [your-nephio-project-id]...
Operation "operations/acat.p2-NNNNNNNNNNNNNN-f5dd29ea-a6c1-424d-ad15-5d563f7c68d1" finished successfully.
Projects must be associated with a billing account, which may be done in the console. Again, your organization may have specific processes and method for selecting and assigning billing accounts. See the project billing account documentation, or consult with the GCP administrators in your organization.
Next, set the new project as the default in your gcloud configuration:
gcloud config set project $PROJECT
The output is similar to:
Updated property [core/project].
Next, enable the GCP services you will need:
gcloud services enable krmapihosting.googleapis.com \
container.googleapis.com \
cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com \
serviceusage.googleapis.com \
iam.googleapis.com \
gkehub.googleapis.com \
anthosconfigmanagement.googleapis.com \
anthos.googleapis.com \
sourcerepo.googleapis.com
The output is similar to:
Operation "operations/acat.p2-NNNNNNNNNNNNN-c1aeadbe-3593-48a4-b4a9-e765e18a3009" finished successfully.
Next, we are going to create service accounts for Config Sync and Porch on the workload clusters to use to access their repositories. The authentication will happen via Workload Identity, so we will also configure the service accounts to allow that.
It is also possible to use Config Controller to create separate service accounts for each cluster, but for simplicity we will use a single one for all clusters, for each workload (Config Sync and Porch).
Create the Config Sync SA:
gcloud iam service-accounts create nephio-config-sync \
--description="Source reader SA for Config Sync" \
--display-name="nephio-config-sync"
The output is similar to:
Created service account [nephio-config-sync].
Create the Porch SA:
gcloud iam service-accounts create nephio-porch \
--description="Service account for Porch" \
--display-name="nephio-porch"
The output is similar to:
Created service account [nephio-porch].
Grant repository read privileges to the Config Sync SA:
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${PROJECT} \
--member "serviceAccount:nephio-config-sync@${PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role roles/source.reader
The output is similar to:
Updated IAM policy for project [your-nephio-project-id].
bindings:
- members:
- serviceAccount:service-NNNNNNNNNNNNN@gcp-sa-anthosconfigmanagement.iam.gserviceaccount.com
role: roles/anthosconfigmanagement.serviceAgent
- members:
- serviceAccount:NNNNNNNNNNNNN@cloudbuild.gserviceaccount.com
role: roles/cloudbuild.builds.builder
- members:
- serviceAccount:service-NNNNNNNNNNNNN@gcp-sa-cloudbuild.iam.gserviceaccount.com
role: roles/cloudbuild.serviceAgent
- members:
- serviceAccount:service-NNNNNNNNNNNNN@compute-system.iam.gserviceaccount.com
role: roles/compute.serviceAgent
- members:
- group:admins@example.com
role: roles/compute.storageAdmin
- members:
- serviceAccount:service-NNNNNNNNNNNNN@container-engine-robot.iam.gserviceaccount.com
role: roles/container.serviceAgent
- members:
- serviceAccount:service-NNNNNNNNNNNNN@containerregistry.iam.gserviceaccount.com
role: roles/containerregistry.ServiceAgent
- members:
- serviceAccount:NNNNNNNNNNNNN-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com
- serviceAccount:NNNNNNNNNNNNN@cloudservices.gserviceaccount.com
- serviceAccount:service-NNNNNNNNNNNNN@gcp-sa-yakima.iam.gserviceaccount.com
role: roles/editor
- members:
- serviceAccount:service-NNNNNNNNNNNNN@gcp-sa-gkehub.iam.gserviceaccount.com
role: roles/gkehub.serviceAgent
- members:
- serviceAccount:service-NNNNNNNNNNNNN@gcp-sa-krmapihosting.iam.gserviceaccount.com
role: roles/krmapihosting.serviceAgent
- members:
- serviceAccount:service-NNNNNNNNNNNNN@gcp-sa-mcmetering.iam.gserviceaccount.com
role: roles/multiclustermetering.serviceAgent
- members:
- serviceAccount:service-NNNNNNNNNNNNN@gcp-sa-yakima.iam.gserviceaccount.com
- user:your-gcp-account@example.com
role: roles/owner
- members:
- serviceAccount:nephio-config-sync@your-nephio-project-id.iam.gserviceaccount.com
role: roles/source.reader
etag: BwYE4Sxmm5A=
version: 1
Grant repository read/write access to the Porch SA:
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${PROJECT} \
--member "serviceAccount:nephio-porch@${PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role roles/source.writer
The Porch SA will also be used for synchronizing GKE Fleet information to the Nephio cluster, for use in our deployments. For this, it needs the roles/gkehub.viewer role:
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${PROJECT} \
--member "serviceAccount:nephio-porch@${PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role roles/gkehub.viewer
Enable the Kubernetes service account to authenticate as Config Sync SA using workload identity:
gcloud iam service-accounts add-iam-policy-binding \
--role roles/iam.workloadIdentityUser \
--member "serviceAccount:${PROJECT}.svc.id.goog[config-management-system/root-reconciler]" \
nephio-config-sync@${PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com
The output is similar to:
Updated IAM policy for serviceAccount [nephio-config-sync@your-nephio-project-id.iam.gserviceaccount.com].
bindings:
- members:
- serviceAccount:your-nephio-project-id.svc.id.goog[config-management-system/root-reconciler]
role: roles/iam.workloadIdentityUser
etag: BwYE4TKYQSk=
version: 1
Enable the Porch server Kubernetes service account (KSA) to authenticate as Porch SA using workload identity:
gcloud iam service-accounts add-iam-policy-binding \
--role roles/iam.workloadIdentityUser \
--member "serviceAccount:${PROJECT}.svc.id.goog[porch-system/porch-server]" \
nephio-porch@${PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com
The Porch controllers also need access, so also allow that KSA to act as the Google service account:
gcloud iam service-accounts add-iam-policy-binding \
--role roles/iam.workloadIdentityUser \
--member "serviceAccount:${PROJECT}.svc.id.goog[porch-system/porch-controllers]" \
nephio-porch@${PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com
Your project should now be ready to proceed with the installation.
Provisioning Config Controller
You can manage GCP infrastructure, including GKE clusters and many other GCP resources using Kubernetes Config Connector, an open source project from Google. The easiest way to run it, though, is by using the hosted version running in Anthos Config Controller.
We will use it to provision our Nephio management cluster and related infrastructure, as well as connect it to Nephio for provisioning of GCP infrastructure by Nephio itself.
You can use the commands below, or for additional details, see the instructions to create a Config Controller instance in your project. If you follow that guide, do not configure Config Sync yet; you will do that later in these instructions, after we create the repository.
gcloud anthos config controller create nephio-cc \
--location=$REGION \
--full-management
Note
The Config Controller clusters are always regional and are not available in all regions. See the link above for a list of available regions. The Config Controller creation may take up to fifteen minutes.The output is similar to:
Create request issued for: [nephio-cc]
Waiting for operation [projects/your-nephio-project-id/locations/us-central1/operations/operation-1693351134043-6041808d31cac-44c9513a-128be132] to complete...done.
Created instance [nephio-cc].
Fetching cluster endpoint and auth data.
kubeconfig entry generated for krmapihost-nephio-cc.
After completing, your kubectl context will be pointing to the Config
Controller cluster:
kubectl config get-contexts
The output is similar to:
CURRENT NAME CLUSTER AUTHINFO NAMESPACE
* gke_your-nephio-project-id_us-central1_krmapihost-nephio-cc gke_your-nephio-project-id_us-central1_krmapihost-nephio-cc gke_your-nephio-project-id_us-central1_krmapihost-nephio-cc
If not, you should retrieve the credentials with:
gcloud anthos config controller get-credentials nephio-cc --location $REGION
There is one more step - granting privileges to the CC cluster to manage GCP resources in this project. With kubectl pointing at the CC cluster, retrieve the service account email address used by CC:
export SA_EMAIL="$(kubectl get ConfigConnectorContext -n config-control \
-o jsonpath='{.items[0].spec.googleServiceAccount}' 2> /dev/null)"
echo $SA_EMAIL
The output is similar to:
service-NNNNNNNNNNNN@gcp-sa-yakima.iam.gserviceaccount.com
Grant that service account roles/editor, which allows full management access to the project, except for IAM and a few other things:
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT \
--member "serviceAccount:${SA_EMAIL}" \
--role roles/editor \
--project $PROJECT
The output is similar to:
Updated IAM policy for project [your-nephio-project-id].
bindings:
- members:
- serviceAccount:NNNNNNNNNNNNN@cloudbuild.gserviceaccount.com
role: roles/cloudbuild.builds.builder
- members:
- serviceAccount:service-NNNNNNNNNNNNN@gcp-sa-cloudbuild.iam.gserviceaccount.com
role: roles/cloudbuild.serviceAgent
- members:
- serviceAccount:service-NNNNNNNNNNNNN@compute-system.iam.gserviceaccount.com
role: roles/compute.serviceAgent
- members:
- group:admins@example.com
role: roles/compute.storageAdmin
- members:
- serviceAccount:service-NNNNNNNNNNNNN@container-engine-robot.iam.gserviceaccount.com
role: roles/container.serviceAgent
- members:
- serviceAccount:service-NNNNNNNNNNNNN@containerregistry.iam.gserviceaccount.com
role: roles/containerregistry.ServiceAgent
- members:
- serviceAccount:NNNNNNNNNNNNN-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com
- serviceAccount:NNNNNNNNNNNNN@cloudservices.gserviceaccount.com
- serviceAccount:service-NNNNNNNNNNNNN@gcp-sa-yakima.iam.gserviceaccount.com
role: roles/editor
- members:
- serviceAccount:service-NNNNNNNNNNNNN@gcp-sa-krmapihosting.iam.gserviceaccount.com
role: roles/krmapihosting.serviceAgent
- members:
- serviceAccount:service-NNNNNNNNNNNNN@gcp-sa-yakima.iam.gserviceaccount.com
- user:your-gcp-account@example.com
role: roles/owner
- members:
- serviceAccount:config-sync-sa@your-nephio-project-id.iam.gserviceaccount.com
role: roles/source.reader
etag: BwYEGPcbq9U=
version: 1
The service account also needs to create Cloud Source Repositories which is not par of the roles/editor, role. So, add the roles/source.admin role as well:
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT \
--member "serviceAccount:${SA_EMAIL}" \
--role roles/source.admin \
--project $PROJECT
Granting IAM privileges is not necessary for this setup, but if you did want to use separate service accounts per workload cluster, you would need to grant those privileges as well (roles/owner for example).
Setting Up GitOps for Config Controller
Next, you will set up a repository to store our GCP configurations, and Config Sync to apply those configurations to Config Controller.
First, create a repository:
gcloud source repos create config-control
The output is similar to:
Created [config-control].
WARNING: You may be billed for this repository. See https://cloud.google.com/source-repositories/docs/pricing for details.
Next, clone that repository locally. You will use this clone shortly.
gcloud source repos clone config-control
The output is similar to:
Cloning into '/home/your-username/nephio-install/config-control'...
warning: You appear to have cloned an empty repository.
Project [your-nephio-project-id] repository [config-control] was cloned to [/home/your-username/nephio-install/config-control].
Before you start adding things to that repository, set up Config Sync to pull configurations from there by creating a RootSync in Config Controller. There is a package available to help properly configure the RootSync:
kpt pkg get --for-deployment https://github.com/nephio-project/catalog.git/distros/gcp/cc-rootsync@main
The output is similar to:
Package "cc-rootsync":
Fetching https://github.com/nephio-project/catalog@main
From https://github.com/nephio-project/catalog
* branch main -> FETCH_HEAD
+ 8519ba9...65bb71f main -> origin/main (forced update)
Adding package "distros/gcp/cc-rootsync".
Fetched 1 package(s).
Customizing package for deployment.
[RUNNING] "builtins/gen-pkg-context"
[PASS] "builtins/gen-pkg-context" in 0s
Results:
[info]: generated package context
Customized package for deployment.
You need to add your project ID to your clone of the package. You can manually edit the gcp-context.yaml or run the following command:
kpt fn eval cc-rootsync --image gcr.io/kpt-fn/search-replace:v0.2.0 --match-name gcp-context -- 'by-path=data.project-id' "put-value=${PROJECT}"
The output is similar to:
[RUNNING] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/search-replace:v0.2.0" on 1 resource(s)
[PASS] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/search-replace:v0.2.0" in 600ms
Results:
[info] data.project-id: Mutated field value to "your-nephio-project-id"
Then, render the package to make sure that the project ID is put in all the right places:
kpt fn render cc-rootsync/
The output is similar to:
Package "cc-rootsync":
[RUNNING] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/apply-replacements:v0.1.1"
[PASS] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/apply-replacements:v0.1.1" in 600ms
[RUNNING] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/apply-setters:v0.2.0"
[PASS] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/apply-setters:v0.2.0" in 500ms
Results:
[info] spec.git.repo: set field value to "https://source.developers.google.com/p/your-nephio-project-id/r/config-control"
[info] spec.git.gcpServiceAccountEmail: set field value to "nephio-config-sync@your-nephio-project-id.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
Successfully executed 2 function(s) in 1 package(s).
In the sandbox exercises, you may have used kpt live apply to apply the package at this point. In this case, there are
restrictions in Config Controller that interfere with the operation of kpt live. So, instead, you can just directly
apply the RootSync resources with kubectl:
kubectl apply -f cc-rootsync/rootsync.yaml
The output is similar to:
rootsync.configsync.gke.io/root-sync created
Config Sync will now synchronize that repository to your Config Controller.
Provisioning Your Management Cluster
You will use CC to provision the Nephio management cluster and associated resources, by way of the config-control repository. The cc-cluster-gke-std-csr-cs package uses CC to create a cluster and a cloud source repository, add the cluster to a fleet, and install and configure Config Sync on the cluster to point to the new repository. This is similar to what the nephio-workload-cluster package does in the Sandbox exercises, except that it uses GCP services to create the repository and bootstrap Config Sync, rather than Nephio controllers.
First, pull the cluster package into your clone of the config-control repository:
cd config-control
kpt pkg get --for-deployment https://github.com/nephio-project/catalog.git/infra/gcp/cc-cluster-gke-std-csr-cs@main nephio
Before we start making changes to the package, it can be helpful to create a local git commit (do not push to the repository until the package is fully configured). This is not mandatory.
git add nephio
git commit -m "Initial clone of GKE package"
Next, configure the package for your environment. Specifically, you need to add your project ID and location to your clone of the package. You can manually edit the gcp-context.yaml or run the following commands:
kpt fn eval nephio --image gcr.io/kpt-fn/search-replace:v0.2.0 --match-name gcp-context -- 'by-path=data.project-id' "put-value=${PROJECT}"
kpt fn eval nephio --image gcr.io/kpt-fn/search-replace:v0.2.0 --match-name gcp-context -- 'by-path=data.location' "put-value=${LOCATION}"
The output is similar to:
[RUNNING] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/search-replace:v0.2.0" on 1 resource(s)
[PASS] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/search-replace:v0.2.0" in 600ms
Results:
[info] data.project-id: Mutated field value to "your-nephio-project-id"
and
[RUNNING] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/search-replace:v0.2.0" on 1 resource(s)
[PASS] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/search-replace:v0.2.0" in 600ms
Results:
[info] data.location: Matched field value "us-central1"
Propagate those changes throughout the package by running the function pipeline:
kpt fn render nephio
If you did the earlier commit, you can run git diff to see all the changes made by the functions. If everything looks
correct, you now commit the changes and push them to the upstream Git repository. From there, Config Sync will apply
the package to the Config Controller (we do not use kpt live apply, instead we rely on Config Sync running in the
Config Controller):
git add .
git commit -m "Fully configured Nephio management cluster package"
git push
To check the status, use the console:
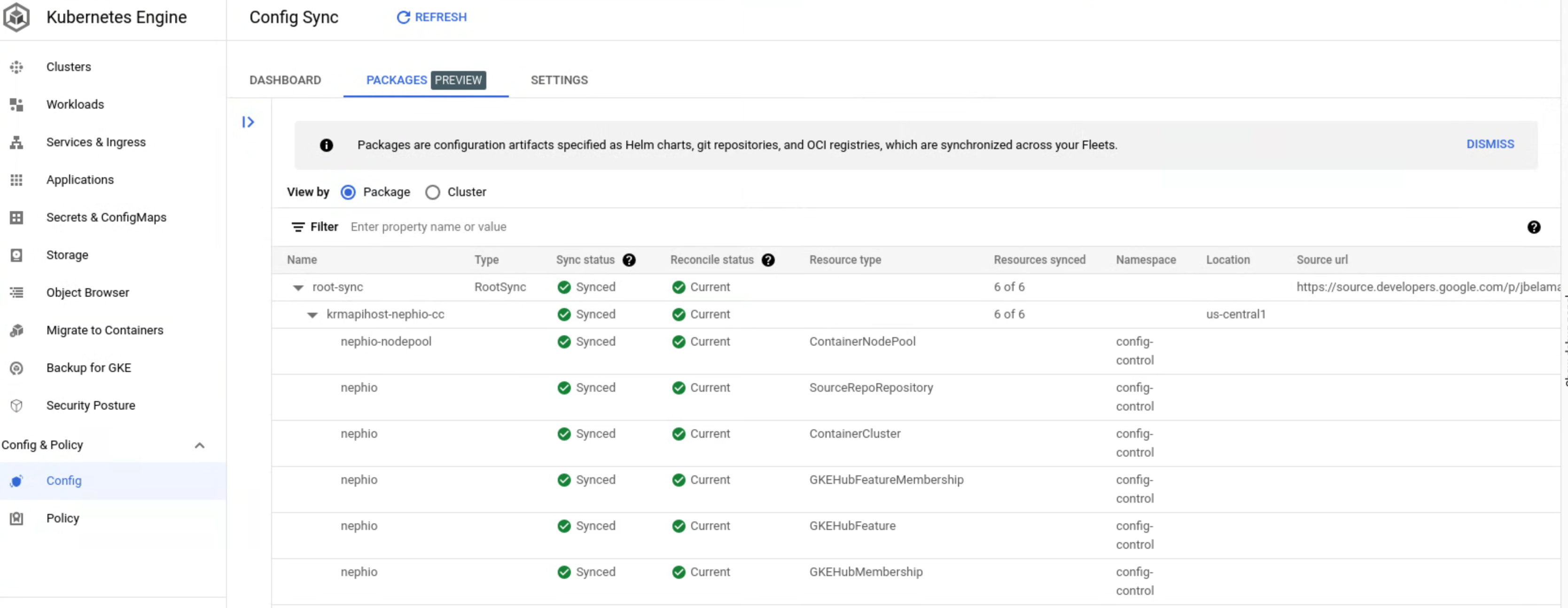
Alternatively, you can use kubectl to view the status of the root-sync:
kubectl describe rootsync -n config-management-system root-sync
The output is similar to:
Name: root-sync
Namespace: config-management-system
Labels: <none>
Annotations: internal.kpt.dev/upstream-identifier: configsync.gke.io|rootsync|config-management-system|root-sync
API Version: configsync.gke.io/v1beta1
Kind: rootsync
Metadata:
Creation Timestamp: 2023-09-11T16:31:50Z
Generation: 1
Resource Version: 14042489
UID: b9263ba3-7d38-4be6-ac16-894a29f61bf8
Spec:
Git:
Auth: gcpserviceaccount
Branch: main
Dir: /
Gcp Service Account Email: nephio-config-sync@your-nephio-project-id.iam.gserviceaccount.com
Repo: https://source.developers.google.com/p/your-nephio-project-id/r/config-control
Source Format: unstructured
Source Type: git
Status:
Conditions:
Last Transition Time: 2023-09-11T16:32:31Z
Last Update Time: 2023-09-11T16:32:31Z
Status: False
Type: Reconciling
Commit: 583f9496783695bc94f8a6afc787cc012731e98e
Error Summary:
Last Transition Time: 2023-09-11T17:32:12Z
Last Update Time: 2023-09-11T17:32:12Z
Message: Sync Completed
Reason: Sync
Status: False
Type: Syncing
Last Synced Commit: 583f9496783695bc94f8a6afc787cc012731e98e
Observed Generation: 1
Reconciler: root-reconciler
Rendering:
Commit: 583f9496783695bc94f8a6afc787cc012731e98e
Error Summary:
Git Status:
Branch: main
Dir: .
Repo: https://source.developers.google.com/p/your-nephio-project-id/r/config-control
Revision: HEAD
Last Update: 2023-09-11T16:32:38Z
Message: Rendering skipped
Source:
Commit: 583f9496783695bc94f8a6afc787cc012731e98e
Error Summary:
Git Status:
Branch: main
Dir: .
Repo: https://source.developers.google.com/p/your-nephio-project-id/r/config-control
Revision: HEAD
Last Update: 2023-09-11T17:32:10Z
Sync:
Commit: 583f9496783695bc94f8a6afc787cc012731e98e
Error Summary:
Git Status:
Branch: main
Dir: .
Repo: https://source.developers.google.com/p/your-nephio-project-id/r/config-control
Revision: HEAD
Last Update: 2023-09-11T17:32:12Z
Events: <none>
You can check if the management cluster is up an running:
gcloud container clusters list
The output is similar to:
NAME LOCATION MASTER_VERSION MASTER_IP MACHINE_TYPE NODE_VERSION NUM_NODES STATUS
krmapihost-nephio-cc us-central1 1.27.3-gke.100 35.xxx.xx.xx e2-medium 1.27.3-gke.100 3 RUNNING
nephio us-central1 1.27.3-gke.100 34.xxx.xx.xx e2-medium 1.27.3-gke.100 3 RUNNING
Once the management cluster is RUNNING, retrieve the credentials and store them as a kubectl context:
gcloud container clusters get-credentials --location $LOCATION nephio
This will also set it to the current context, which you can verify with:
kubectl config get-contexts
The output is similar to:
CURRENT NAME CLUSTER AUTHINFO NAMESPACE
* gke_your-nephio-project-id_us-central1_nephio gke_your-nephio-project-id_us-central1_nephio gke_your-nephio-project-id_us-central1_nephio
gke_your-nephio-project-id_us-central1_krmapihost-nephio-cc gke_your-nephio-project-id_us-central1_krmapihost-nephio-cc gke_your-nephio-project-id_us-central1_krmapihost-nephio-cc
If the context is not current, use this command to make it current:
kubectl config use-context "gke_${PROJECT}_${LOCATION}_nephio"
As a final step, return to the nephio-install directory as your current working directory:
cd ..
Installing the Nephio Components
You will use GitOps to install the Nephio components in the management cluster. As part of the previous management cluster provisioning, a repository was created for managing the Nephio cluster with GitOps. To verify:
gcloud source repos list
The output is similar to:
REPO_NAME PROJECT_ID URL
config-control your-nephio-project-id https://source.developers.google.com/p/your-nephio-project-id/r/config-control
nephio your-nephio-project-id https://source.developers.google.com/p/your-nephio-project-id/r/nephio
Ensure your current working directory is nephio-install, and then clone the nephio repository locally:
gcloud source repos clone nephio
The output is similar to:
Cloning into '/home/your-username/nephio-install/nephio'...
warning: You appear to have cloned an empty repository.
Project [your-nephio-project-id] repository [nephio] was cloned to [/home/your-username/nephio-install/nephio].
Navigate to that directory, and pull out the nephio-mgmt package, which contains all the necessary Nephio components as subpackages:
- Porch
- Nephio Controllers
- Network Config Operator
- Resource Backend
- The Nephio WebUI, configured to use Google Cloud OAuth 2.0
- A GCP-specific controller for syncing clusters, fleets, and fleet scopes
cd nephio
kpt pkg get --for-deployment https://github.com/nephio-project/catalog.git/distros/gcp/nephio-mgmt@main
The output is similar to:
Package "nephio-mgmt":
Fetching https://github.com/nephio-project/catalog@main
From https://github.com/nephio-project/catalog
* branch main -> FETCH_HEAD
+ 65bb71f...fd422eb main -> origin/main (forced update)
Adding package "distros/gcp/nephio-mgmt".
Fetched 1 package(s).
Customizing package for deployment.
[RUNNING] "builtins/gen-pkg-context"
[PASS] "builtins/gen-pkg-context" in 500ms
Results:
[info]: generated package context
[info]: generated package context
[info]: generated package context
[info]: generated package context
...(9 line(s) truncated, use '--truncate-output=false' to disable)
Customized package for deployment.
Create a local commit, but do not push it to the upstream repository yet. As before, this is just to allow git diff
to identify the changes you make later.
git add nephio-mgmt/
git commit -m "Initial checking of nephio-mgmt"
The output is similar to:
[main (root-commit) 78af570] Initial checking of nephio-mgmt
133 files changed, 9161 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/Kptfile
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/README.md
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/Kptfile
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/README.md
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/Kptfile
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/README.md
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/controller/clusterrole-approval.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/controller/clusterrole-bootstrap.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/controller/clusterrole-controller.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/controller/clusterrole-network.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/controller/clusterrole-porch.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/controller/clusterrole-repository.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/controller/clusterrole-token.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/controller/clusterrolebinding-approval.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/controller/clusterrolebinding-bootstrap.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/controller/clusterrolebinding-controller.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/controller/clusterrolebinding-network.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/controller/clusterrolebinding-porch.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/controller/clusterrolebinding-repository.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/controller/clusterrolebinding-token.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/controller/deployment-controller.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/controller/deployment-token-controller.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/controller/role-leader-election.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/controller/rolebinding-leader-election.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/controller/serviceaccount-controller.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app/package-context.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/crd/Kptfile
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/crd/README.md
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/crd/bases/config.nephio.org_networks.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/crd/bases/infra.nephio.org_clustercontexts.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/crd/bases/infra.nephio.org_networkconfigs.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/crd/bases/infra.nephio.org_networks.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/crd/bases/infra.nephio.org_repositories.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/crd/bases/infra.nephio.org_tokens.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/crd/bases/infra.nephio.org_workloadclusters.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/crd/bases/req.nephio.org_capacities.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/crd/bases/req.nephio.org_datanetworknames.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/crd/bases/req.nephio.org_datanetworks.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/crd/bases/req.nephio.org_interfaces.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/crd/bases/workload.nephio.org_amfdeployments.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/crd/bases/workload.nephio.org_smfdeployments.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/crd/bases/workload.nephio.org_upfdeployments.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/crd/package-context.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/namespace.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/package-context.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/network-config/Kptfile
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/network-config/README.md
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/network-config/app/Kptfile
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/network-config/app/README.md
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/network-config/app/controller/clusterrole-controller.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/network-config/app/controller/clusterrole-network.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/network-config/app/controller/clusterrole-target.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/network-config/app/controller/clusterrolebinding-controller.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/network-config/app/controller/clusterrolebinding-network.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/network-config/app/controller/clusterrolebinding-target.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/network-config/app/controller/deployment-controller.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/network-config/app/controller/role-leader-election.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/network-config/app/controller/rolebinding-leader-election.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/network-config/app/controller/serviceaccount-controller.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/network-config/app/package-context.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/network-config/crd/Kptfile
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/network-config/crd/README.md
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/network-config/crd/package-context.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/network-config/namespace.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/network-config/package-context.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/package-context.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/porch/0-packagerevs.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/porch/0-packagevariants.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/porch/0-packagevariantsets.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/porch/0-repositories.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/porch/1-namespace.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/porch/2-function-runner.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/porch/3-porch-server.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/porch/4-apiservice.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/porch/5-rbac.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/porch/6-rbac-bind.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/porch/7-auth-reader.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/porch/8-auth-delegator.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/porch/9-controllers.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/porch/9-porch-controller-clusterrole.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/porch/9-porch-controller-packagevariants-clusterrole.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/porch/9-porch-controller-packagevariants-clusterrolebinding.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/porch/9-porch-controller-packagevariantsets-clusterrole.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/porch/9-porch-controller-packagevariantsets-clusterrolebinding.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/porch/Kptfile
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/porch/package-context.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/Kptfile
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/README.md
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/app/Kptfile
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/app/README.md
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/app/controller/clusterrole-controller.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/app/controller/clusterrolebinding-controller.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/app/controller/deployment-controller.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/app/controller/grpc/service-grpc.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/app/controller/role-leader-election.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/app/controller/rolebinding-leader-election.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/app/controller/serviceaccount-controller.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/app/package-context.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/crd/Kptfile
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/crd/README.md
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/crd/bases/inv.nephio.org_endpoints.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/crd/bases/inv.nephio.org_links.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/crd/bases/inv.nephio.org_nodes.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/crd/bases/inv.nephio.org_targets.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/crd/bases/ipam.resource.nephio.org_ipclaims.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/crd/bases/ipam.resource.nephio.org_ipprefixes.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/crd/bases/ipam.resource.nephio.org_networkinstances.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/crd/bases/topo.nephio.org_rawtopologies.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/crd/bases/vlan.resource.nephio.org_vlanclaims.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/crd/bases/vlan.resource.nephio.org_vlanindices.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/crd/bases/vlan.resource.nephio.org_vlans.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/crd/package-context.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/namespace.yaml
create mode 100644 nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/package-context.yaml
Prior to deploying the package, we need to manually setup the secret for the WebUI.
See Google OAuth 2.0 or OIDC for details on how to set up OAuth. In particular you need to create the client ID and the secret manually.
The nephio-webui subpackage in nephio-mgmt is already set up for Google OAuth 2.0; you can follow the instructions in the linked document if you prefer OIDC.
Once, you have created the namespace and secret, set the GCP project ID and location in the package:
kpt fn eval nephio-mgmt --image gcr.io/kpt-fn/search-replace:v0.2.0 --match-name gcp-context -- 'by-path=data.project-id' "put-value=${PROJECT}"
kpt fn eval nephio-mgmt --image gcr.io/kpt-fn/search-replace:v0.2.0 --match-name gcp-context -- 'by-path=data.location' "put-value=${LOCATION}"
kpt fn eval nephio-mgmt --image gcr.io/kpt-fn/search-replace:v0.2.0 --match-name gen-app-config -- 'by-path=params.hostname' "put-value=${WEBUIFQDN}"
The output is similar to:
[RUNNING] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/search-replace:v0.2.0" on 2 resource(s)
[PASS] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/search-replace:v0.2.0" in 600ms
Results:
[info] data.project-id: Mutated field value to "your-nephio-project-id"
[info] data.project-id: Mutated field value to "your-nephio-project-id"
and
[RUNNING] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/search-replace:v0.2.0" on 2 resource(s)
[PASS] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/search-replace:v0.2.0" in 600ms
Results:
[info] data.location: Mutated field value to "us-central1"
[info] data.location: Mutated field value to "us-central1"
and
[RUNNING] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/search-replace:v0.2.0" on 1 resource(s)
[PASS] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/search-replace:v0.2.0" in 1.1s
Results:
[info] params.hostname: Mutated field value to "nephio.example.com"
Render the package:
kpt fn render nephio-mgmt/
The output is similar to:
Package "nephio-mgmt/cert-manager":
Package "nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/app":
Package "nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers/crd":
Package "nephio-mgmt/nephio-controllers":
Package "nephio-mgmt/nephio-webui":
[RUNNING] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/apply-replacements:v0.1.1"
[PASS] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/apply-replacements:v0.1.1" in 700ms
[RUNNING] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/starlark:v0.5.0"
[PASS] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/starlark:v0.5.0" in 600ms
[RUNNING] "docker.io/nephio/gen-configmap-fn:2023-09-14-01"
[PASS] "docker.io/nephio/gen-configmap-fn:2023-09-14-01" in 500ms
Package "nephio-mgmt/network-config/app":
Package "nephio-mgmt/network-config/crd":
Package "nephio-mgmt/network-config":
Package "nephio-mgmt/porch":
[RUNNING] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/apply-replacements:v0.1.1"
[PASS] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/apply-replacements:v0.1.1" in 700ms
[RUNNING] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/apply-setters:v0.2.0"
[PASS] "gcr.io/kpt-fn/apply-setters:v0.2.0" in 600ms
Results:
[info] spec.git.repo: set field value to "https://source.developers.google.com/p/your-nephio-project-id/r/config-control"
[info] spec.git.repo: set field value to "https://source.developers.google.com/p/your-nephio-project-id/r/nephio"
[info] metadata.annotations.iam.gke.io/gcp-service-account: set field value to "nephio-porch@your-nephio-project-id.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
Package "nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/app":
Package "nephio-mgmt/resource-backend/crd":
Package "nephio-mgmt/resource-backend":
Package "nephio-mgmt":
Successfully executed 5 function(s) in 13 package(s).
Commit the rendered package, and push the changes to the repository so Config Sync can pick them up and apply them.
git add .
git commit -m "Fully configured Nephio component package"
git push
You should also tag the package, to make it manageable with Nephio/Porch for any future edits:
git tag nephio-mgmt/v1
git push --tags
The output is similar to:
Total 0 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
To https://source.developers.google.com/p/your-nephio-project-id/nephio
* [new tag] nephio-mgmt/v1 -> nephio-mgmt/v1
Accessing Nephio
Accessing Nephio with kubectl or kpt can be done from your workstation, so long as you use the context for the Nephio management cluster.
To access the WebUI, you need to create a DNS entry pointing to the load balancer IP serving the Ingress resources. The Ingress included in the Web UI package will use Cert Manager to automatically generate a self-signed certificate for the WEBUIFQDN value.
Find the IP address using this command:
INGRESS_IP=$(kubectl -n nephio-webui get ingress nephio-webui -o jsonpath="{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}")
echo $INGRESS_IP
The output is similar to:
1.2.3.4
You will need to add this as an A record for the name you used in WEBUIFQDN. If you are using Google Cloud DNS for that zone, first find the managed zone name:
gcloud dns managed-zones list
The output is similar to:
NAME DNS_NAME DESCRIPTION VISIBILITY
gke-krmapihost-nephio-cc-6e7c24f5-dns cluster.local. Private zone for GKE cluster "krmapihost-nephio-cc" with cluster suffix "cluster.local." in project "your-nephio-project-id" with scope "CLUSTER_SCOPE" private
your-managed-zone-name example.com. public
In this case, you would use your-managed-zone-name, which is the name for the example.com. zone.
Start a transaction to add a record set:
gcloud dns record-sets transaction start --zone=$MANAGED_ZONE
The output is similar to:
Transaction started [transaction.yaml].
Add the specific IP address as an A record, with the fully-qualified domain name of the site:
gcloud dns record-sets transaction add $INGRESS_IP \
--name=$WEBUIFQDN \
--ttl=300 \
--type=A \
--zone=$MANAGED_ZONE
The output is similar to:
Record addition appended to transaction at [transaction.yaml].
Run the transaction to store the record. Depending on your DNS configuration, it may take some time to be resolvable.
gcloud dns record-sets transaction execute --zone=$MANAGED_ZONE
The output is similar to:
Executed transaction [transaction.yaml] for managed-zone [your-managed-zone-name].
Created [https://dns.googleapis.com/dns/v1/projects/your-nephio-project-id/managedZones/your-managed-zone-name/changes/1].
ID START_TIME STATUS
1 2023-09-15T19:38:36.601Z pending
You can now access the site via your browser, and will be asked to login as shown below:
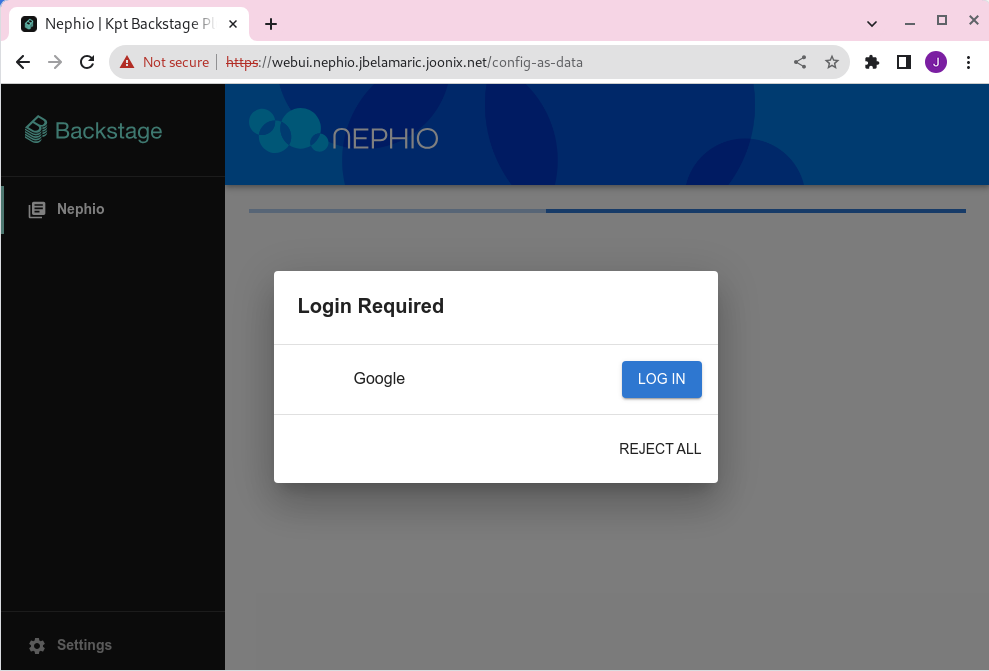
Some Exercises
As a an exercise to get started, you can create edge clusters by using kubectl to apply the following
PackageVariantSet to your management cluster:
apiVersion: config.porch.kpt.dev/v1alpha2
kind: PackageVariantSet
metadata:
name: edge-clusters
spec:
upstream:
repo: blueprints-infra-gcp
package: nephio-workload-cluster-gke
revision: main
targets:
- repositories:
- name: nephio
packageNames:
- edge01
- edge02
- edge03
template:
annotations:
approval.nephio.org/policy: initial
injectors:
- kind: ConfigMap
name: gcp-context
pipeline:
mutators:
- image: gcr.io/kpt-fn/set-labels:v0.2.0
configMap:
nephio.org/site-type: edge
nephio.org/region: us-central1
This uses the GCP context (project and location) that was added to the cluster when you created the management cluster to create the GKE edge clusters, their Google Cloud Source Repositories, and attach them to Nephio.
As a follow up exercise, you could try creating GCP context ConfigMap entries for different locations, and use a PackageVariantSet to create per-location edge clusters based on a label selector against those.
First, create GCP context ConfigMap for each zone:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
labels:
nephio.org/site-type: zonal
nephio.org/region: us-west1
nephio.org/zone: us-west1-a
name: gcp-context-us-west1-a
data:
location: us-west1-a
project-id: your-nephio-project-id
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
labels:
nephio.org/site-type: zonal
nephio.org/region: us-west1
nephio.org/zone: us-west1-b
name: gcp-context-us-west1-b
data:
location: us-west1-b
project-id: your-nephio-project-id
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
labels:
nephio.org/site-type: zonal
nephio.org/region: us-west1
nephio.org/zone: us-west1-c
name: gcp-context-us-west1-c
data:
location: us-west1-c
project-id: your-nephio-project-id
Then, create a PackageVariantSet that selects based upon those:
apiVersion: config.porch.kpt.dev/v1alpha2
kind: PackageVariantSet
metadata:
name: uswest1-zonal-clusters
spec:
upstream:
repo: blueprints-infra-gcp
package: nephio-workload-cluster-gke
revision: main
targets:
- objectSelector:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
matchLabels:
nephio.org/site-type: zonal
nephio.org/region: us-west1
template:
downstream:
repo: nephio
packageExpr: "'zonal-gke-' + target.labels['nephio.org/zone']"
annotations:
approval.nephio.org/policy: initial
injectors:
- kind: ConfigMap
nameExpr: target.name
pipeline:
mutators:
- image: gcr.io/kpt-fn/set-labels:v0.2.0
configMap:
nephio.org/site-type: zonal
configMapExprs:
- key: nephio.org/region
valueExpr: target.labels["nephio.org/region"]
- key: nephio.org/zone
valueExpr: target.labels["nephio.org/zone"]
Future Considerations
Updating this installation and integrating the exercises with GKE Network Function Optimization would be useful to demonstrate how to build out Nephio-based networks on GCP.
Next Steps
Note
The exercises using free5gc rely on Multus and on the gtp5g kernel module, neither of which are installed on GKE nodes. Therefore, the free5gc workloads cannot be run on this installation. You will need to alter the exercises touse workloads that do not rely on that functionality in order to experiment with Nephio features.
- Step through the Free5GC and OAI exercises
- Dig into the user guide